The F-1 student visa is the most common visa for students wanting to study in the United States. It is a temporary visa for foreign students who enter the United States in order to continue their education at an accredited school or college. In FY 2024, about 400,737 F-1 visas were issued by the United States.
F-1 Student Visa Application Process & Steps
The steps required to apply for an F-1 student visa may vary based on the U.S. embassy or consulate where you choose to submit your application. Visit USEmbassy.Gov to confirm the requirements for your specific U.S. embassy or consulate.
To begin the process of obtaining an F-1 student visa, you’ll need to:
- Fill out the Online Nonimmigrant Visa Application, Form DS-160. Print this application form confirmation page and bring it to your F-1 student visa interview.
- Upload Your Photo –Follow the photograph requirements and submit with the online application.
Upon completing your online application, you proceed to schedule an interview at any U.S. Embassy or Consulate. It’s best to choose an interview location in the area in which you have permanent residency. Apply for your F-1 student visa early because interview wait times will vary based on location and seasons.
F-1 Student Visa Requirements:
- The selected program must be an accredited academic educational program, a language-training program, or a vocational program.
- The student’s school must be accepted by the Student and Exchange Visitors Program as well as Immigration and Customs Enforcement.
- The student must be enrolled as a full-time student.
- The student must be able to demonstrate proficiency in the English language or be enrolled in courses to reach that proficiency.
- The student must have sufficient funds to be financially independent during the course of the study.
- The student must not release his/her acquired residence abroad.
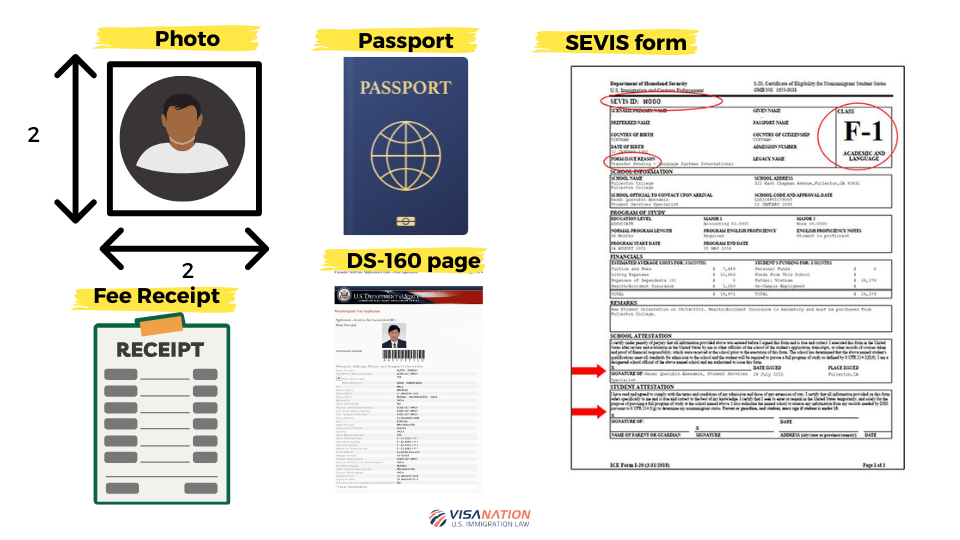
Required Documents for F-1 Visa
There are a few documents that you are required to obtain prior to your F-1 student visa interview and have with you on the interview date. Failing to have these documents can jeopardize the approval of your F-1 student visa.
- Valid Passport – Your passport must be valid for at least six months beyond your period of stay in the United States.
- Nonimmigrant Visa Application, Form DS-160 confirmation page
- Application fee payment receipt
- Photo – If your photo failed to upload while completing your online nonimmigrant visa application, you must bring a printed photo that meets the requirements to the interview.
- Certificate of Eligibility for Nonimmigrant (F-1 or M-1) Student Status, Form I-20 – Your school will send you a SEVIS-generated Form I-20 once they have entered your information in the SEVIS database. You and your school official must sign the Form I-20.
Additional Documents
- Demonstration of your academic preparation, such as:
- Transcripts, diplomas, degrees, or certificates from schools you attended
- Standardized test scores are required by your U.S. school.
- Proof that you intend to depart the United States upon completion of the course of study.
- Proof you can pay all your educational, living, and travel costs
F-1 Visa Interview: What to Expect
At the F-1 student visa interview, digital fingerprints will be taken during the interview and put on file. Consular officials will determine whether you’re qualified and have met all the requirements to be approved for the requested visa category.
After the interview, your visa may undergo further administrative processing, which is resolved within an estimated 60 days after the interview.
Upon approval of the F-1 student visa, you can check the visa processing time to estimate how long before the visa is ready for pick-up or delivery.
Commuter Status: Canada and Mexico
The F-3 Visa is designed for Canadian and Mexican academic commuter students. Essentially, these students are citizens of either Canada or Mexico who wish to study in the United States but maintain in their place of residence.
Students are required to study at an accredited community/junior college, vocational school, or university that is located 75 miles from the U.S. land border port of entry. Students cannot reside in the United States.
Working on F-1 Visa: Permits & Options
Students on an F1 visa are not permitted to work off-campus in their first year. However, they can work on campus under certain regulations. If a student decides to work off-campus with an F-1 visa, their visa might be revoked, and required to leave the country.
After a student’s first year, they may engage in certain types of employment off-campus, provided that it is related to their area of study:
- Curricular Practical Training (CPT) – You can work on CPT either full-time or part-time.
- Optional Practical Training (OPT) (pre-completion or post-completion) – While school is in session, you may only work 20 hours per week.
- Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Optional Practical Training Extension (OPT)
The student must be in legal status and abiding by the conditions of their F-1 student visa to ensure that they maintain their lawful presence in the United States.
F-1 Visa Status to Green Card
Many people who enter the U.S. through work, family, or school may eventually decide they want to make the United States their permanent home. However, transitioning from a nonimmigrant visa to an immigrant visa (green card) isn’t as easy as it sounds, especially for the F-1 Visa. This is because of an attribute known as “dual intent”, which is the ability for the holder of a certain visa to pursue lawful permanent residence while under nonimmigrant status.
Is the F-1 Dual intent?
While some visas have dual intent, such as the H-1B and the L-1, others do not. The F-1 is, unfortunately, not dual intent.
Applying for a green card under F-1 status may not only result in your green card getting denied, but it is also considered a violation of status that may result in a temporary bar from re-entry into the United States.
The question remains: can you get a green card if you entered the U.S. under F-1 status?
Yes, but it’s not a simple matter of transitioning straight from an F-1 to a green card. There are two routes.
1. Transitioning from F-1 to a Green Card Through Marriage
If you met your spouse while studying, you can transition from an F-1 to a green card through adjustment of status, but don’t jump into it without consultation. If you came to the U.S. on F-1 status with the intent to marry, the application will be denied, and at worst, may be considered visa fraud, especially if this occurs before 90 days.
Because of this, it’s critical to consult an immigration lawyer to discuss your circumstances with a skilled F-1 student attorney.
VisaNation law firms has extensive experience in supporting indiviudals to obtain green cards. Contact us today!
2. Transitioning from F-1 to a Green Card Through Work
To transition through work, a student must change their status to a different nonimmigrant visa that has “dual intent” and is permitted under F-1 status. Some options to consider are the
- H-1B
- E-1/E-2
- L-1
- and O-1 visas.
If you qualify for any of these visas, then it’s a matter of filing (or having your employer file) an I-129 petition along with the fees and supporting documentation. In the case of the H-1B, you may have to contend with the annual lottery, which has certain specifications.
Once you’ve obtained your dual intent visa, you will be able to immediately file for your green card. You will have to choose which green card best fits your qualifications. If you are a young student with very little work experience, then you may want to consider the EB-3. If you went to school later in life and have gotten a master’s degree, the EB-2 may be better.
Once you or your employer files the green card petition, you will need to wait until your priority date is current. This is the day that the USCIS obtains your petition. You should be checking the monthly visa bulletin provided by the Department of State. Once the final action date for your green card and country of origin matches or passes your priority date, your date will be current, and a visa number will become available.
At this point, you have two options. Since you are already in the U.S. under a nonimmigrant status, you will be able to simply file Form I-485 to have your status adjusted. This takes an average of 8-12 months and can be costly.
Alternatively, you can elect consular processing, which requires you to complete a DS-260 application at a U.S. Consulate or Embassy in your home country for an interview. This may seem inconvenient, but it may be the faster option depending on the caseload of your consulate.
If your I-485 is approved or your consular interview goes well, you will be granted lawful permanent residence, and your green card will be mailed to you.
Securing Your Student Visa
Obtaining an F-1 student visa is a significant step toward achieving your education goals in the United States. Understanding the F-1 visa eligibility criteria, required documents, and available work options is essential for a smooth application process.
As you prepare to study in the U.S., remember that having the right guidance, such as immigration lawyers experienced in the F-1 visa process, can make all the difference when securing your visa and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Get a Green Card with VisaNation Law Firm
Whether you’re applying for the first time or transitioning to work or permanent residency, staying informed and well-prepared for every step of your journey is critical.
Understanding eligibility and fulfilling requirements is critical for a successful application. The importance of working with experienced immigration lawyers to navigate the F-1 visa process.

How VisaNation Law Group Immigration Lawyers Can Help
If the participant wishes to extend their time in the United States, VisaNation Law Group’s immigration attorneys are well prepared to conduct the F-1 Visa renewal process with you. VisaNation Law Group attorneys will also advise in cases of CPT, OPT, STEM extensions, visa changes, and employment extension using the Cap Gap Rule. If the applicant receives F-1 status, then the holder’s spouse and unmarried, minor children are eligible to obtain an F-2 Visa. Our skilled attorneys are ready to help you.
VisaNation Law Group’s lawyers will assist in obtaining the F-1 Visa and, with extensive experience, deliver the best strategy necessary. The immigration lawyers offer individualized attention in order to provide the utmost, efficient service. F-1 Visa lawyers will be involved in every step of the process, even if the client has made previous attempts unsuccessfully.